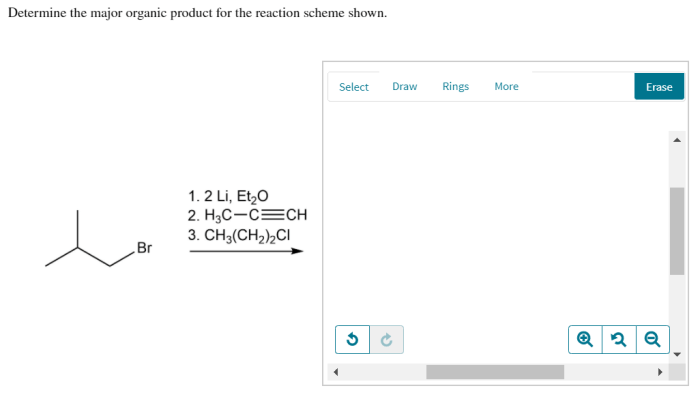
Determine the major organic product for the reaction scheme shown – Determining the major organic product for a given reaction scheme is a crucial aspect of organic chemistry. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of predicting the major product, exploring the factors that influence its formation and the principles that govern its selectivity.
By analyzing the reaction scheme, identifying functional groups, and considering regio- and stereoselectivity, chemists can effectively predict the outcome of organic reactions. This knowledge empowers them to design synthetic strategies, optimize reaction conditions, and develop new and innovative molecules.
Determine the Major Organic Product
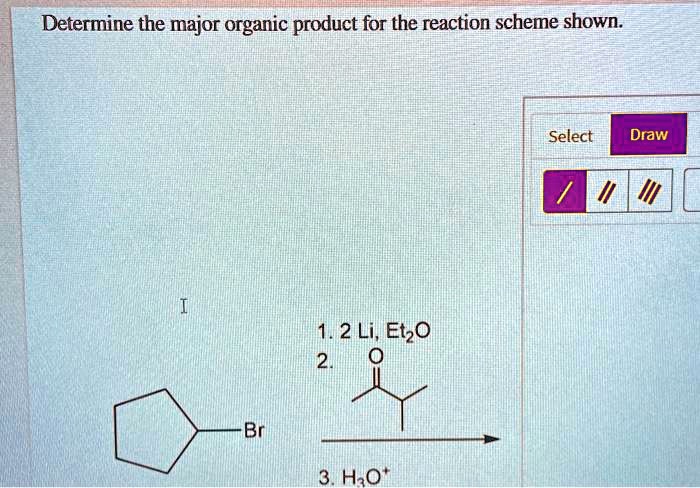
In organic chemistry, the major organic product refers to the most abundant product formed in a chemical reaction. Its formation is influenced by various factors, including the stability, kinetics, and thermodynamics of the reaction.
Analyzing the reaction scheme is crucial for determining the major organic product. The reaction mechanism, functional groups involved, regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and reaction conditions all play significant roles in predicting the outcome of the reaction.
Analyze the Reaction Scheme
The reaction scheme provides a roadmap of the chemical transformation, outlining the reactants, intermediates, and products involved. By understanding the reaction mechanism, one can determine the most likely pathway for the reaction to occur.
Common reaction mechanisms include nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic addition, and radical reactions. Each mechanism has its characteristic features and preferences for certain functional groups.
Identify the Functional Groups, Determine the major organic product for the reaction scheme shown
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within an organic molecule that determine its reactivity. They are responsible for the characteristic reactions of organic compounds.
- Alkanes: C-H bonds
- Alkenes: C=C bonds
- Alkynes: C≡C bonds
- Alcohols: -OH groups
- Aldehydes: -CHO groups
- Ketones: -CO- groups
- Carboxylic acids: -COOH groups
Apply the Principles of Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
Regioselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to occur at a specific site within a molecule, while stereoselectivity refers to the preference for a specific stereoisomer to be formed.
These principles can be applied to predict the major organic product by considering the stability of the intermediates and products formed.
Consider the Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and catalyst, can significantly influence the formation of the major organic product.
For example, higher temperatures may favor thermodynamically stable products, while polar solvents may promote nucleophilic reactions.
Essential Questionnaire: Determine The Major Organic Product For The Reaction Scheme Shown
What is the major organic product?
The major organic product is the product that is formed in the greatest amount in a given reaction.
What factors influence the formation of the major organic product?
The formation of the major organic product is influenced by factors such as stability, kinetics, and thermodynamics.
How can I predict the major organic product?
To predict the major organic product, you need to analyze the reaction scheme, identify functional groups, and consider regio- and stereoselectivity.