Which expression is equivalent to mc016 1 jpg? This question delves into the realm of image file formats, a fundamental aspect of digital imaging that plays a crucial role in determining the appearance, size, and usability of images. Join us as we embark on a comprehensive exploration of image file formats, unraveling their complexities and discovering their practical applications.
In this article, we will delve into the different types of image file formats, their common extensions, and their significance in the digital world. We will also explore the concept of image resolution, understanding its impact on image quality and file size.
Additionally, we will discuss image dimensions and aspect ratios, emphasizing the importance of maintaining these ratios during image resizing.
Image File Formats
Image file formats determine how digital images are stored and processed. Each format has its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses.
Common image file formats include:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): A lossy format known for its small file size and good image quality, often used for web images and photographs.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): A lossless format that supports transparency, making it suitable for graphics and logos.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): A lossless format with limited colors, commonly used for animations and small graphics.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): A lossless format with high image quality, used for professional photography and printing.
- BMP (Bitmap): A lossless format that creates large file sizes, often used for storing uncompressed images.
Image Resolution
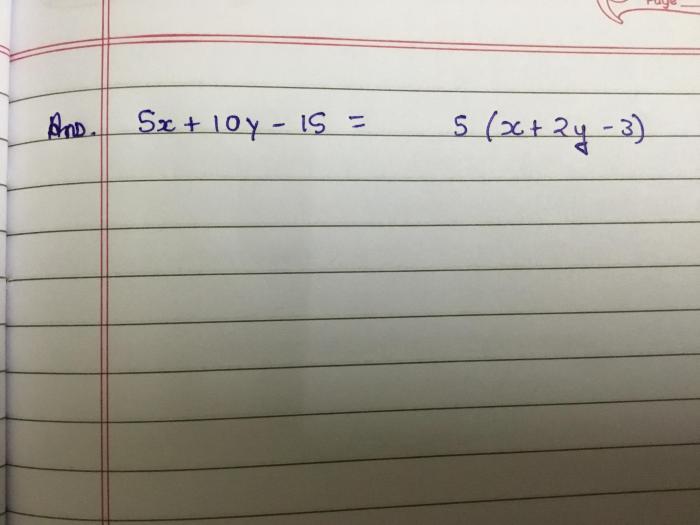
Image resolution refers to the number of pixels per unit of length (usually inches or centimeters) in an image. Higher resolution images have more pixels and finer detail, but also larger file sizes.
The relationship between image resolution and file size is directly proportional. Increasing the resolution increases the number of pixels and therefore the file size.
Tips for optimizing image resolution:
- Use the highest resolution necessary for the intended purpose.
- For web images, 72-150 pixels per inch (PPI) is generally sufficient.
- For print images, 300 PPI or higher is recommended for high-quality prints.
Image Dimensions
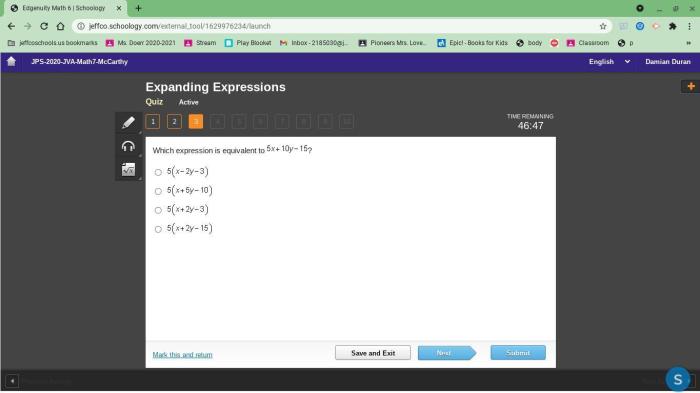
Image dimensions refer to the width and height of an image in pixels. They are expressed as “width x height.”
Common image dimensions include:
| Dimension | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|
| 640 x 480 | 4:3 |
| 800 x 600 | 4:3 |
| 1024 x 768 | 4:3 |
| 1280 x 720 | 16:9 |
| 1920 x 1080 | 16:9 |
Maintaining aspect ratios when resizing images ensures that the image’s proportions are preserved, preventing distortion.
Image Compression
Image compression reduces the file size of an image without significantly affecting its visual quality.
Image compression methods include:
- Lossless compression: Removes redundant data without compromising image quality, but results in larger file sizes.
- Lossy compression: Removes some data to reduce file size, resulting in potential quality loss.
JPEG and PNG support lossy compression, while TIFF and BMP use lossless compression.
Examples of image compression:
- Compressing a JPEG image to reduce its file size for web use.
- Using lossless compression to preserve the quality of a TIFF image for printing.
Image Editing Software

Image editing software allows users to manipulate, enhance, and optimize images.
Popular image editing software includes:
- Adobe Photoshop
- GIMP
- Paint.NET
- Canva
- Pixelmator
Key features of image editing software:
- Cropping and resizing images
- Adjusting image brightness, contrast, and color
- Applying filters and effects
- Removing unwanted objects
- Optimizing images for different purposes
Image Optimization for Web: Which Expression Is Equivalent To Mc016 1 Jpg
Optimizing images for web performance improves website loading times and user experience.
Best practices for image optimization:
- Use the appropriate image format (e.g., JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics).
- Optimize image resolution and dimensions for web display.
- Use image compression to reduce file size.
- Use CSS sprites to combine multiple images into a single file.
- Implement lazy loading to load images only when they are visible to the user.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the performance of your website and enhance the user experience.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between JPEG and PNG?
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a lossy compression format that prioritizes smaller file sizes, making it suitable for images with complex colors and gradients. PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a lossless compression format that preserves image quality, making it ideal for images with sharp lines, text, and transparency.
How do I convert an image to a different file format?
Many image editing software and online tools allow you to convert images between different file formats. Simply open the image in the software, select the desired file format from the “Save As” or “Export” options, and save the image.
What is the optimal image resolution for web use?
For most web applications, an image resolution of 72 pixels per inch (PPI) is sufficient. Higher resolutions may result in larger file sizes and slower loading times, while lower resolutions may compromise image quality.