After blunt trauma to the abdomen a 21 – Blunt abdominal trauma, a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, demands a comprehensive approach to patient care. This article delves into the intricacies of organ injury assessment, hemodynamic management, abdominal imaging, surgical intervention, and non-operative management, providing a comprehensive overview of this critical topic.
The management of blunt abdominal trauma requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving trauma surgeons, radiologists, intensivists, and other specialists. A thorough understanding of the principles and techniques Artikeld in this article is essential for optimal patient outcomes.
Organ Injury Assessment: After Blunt Trauma To The Abdomen A 21
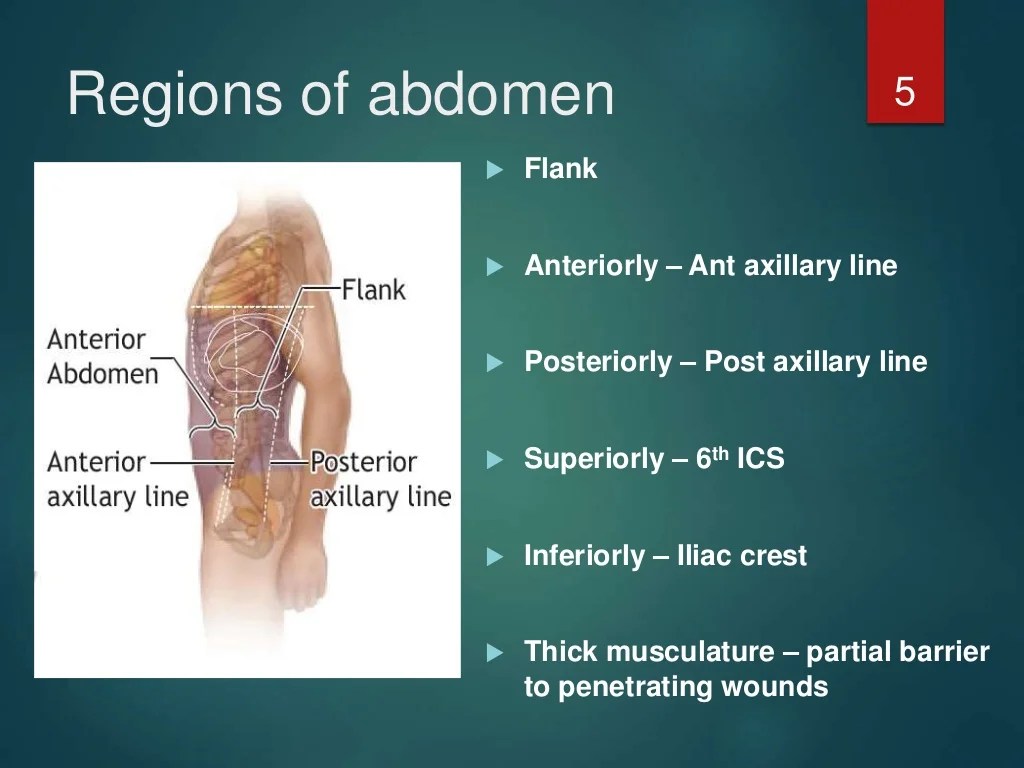
Blunt abdominal trauma can result in injuries to various organ systems. The most commonly affected organs include:
- Liver
- Spleen
- Kidneys
- Pancreas
- Intestines
- Mesentery
Signs and symptoms of specific organ injuries may include:
- Liver:Abdominal pain, tenderness, and distension; elevated liver enzymes
- Spleen:Left upper quadrant pain and tenderness; splenomegaly
- Kidneys:Flank pain, hematuria, and proteinuria
- Pancreas:Epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting; elevated amylase and lipase
- Intestines:Abdominal pain, distension, and guarding; bloody stools
- Mesentery:Abdominal pain and tenderness; peritoneal irritation
Diagnostic tests used to evaluate organ damage after blunt abdominal trauma include:
- Abdominal X-ray:May show free air, organ displacement, or fractures
- Abdominal ultrasound:Can visualize organ parenchyma and detect fluid collections
- Abdominal CT scan:Provides detailed images of organs and can detect occult injuries
- Diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL):Instillation of fluid into the peritoneal cavity to detect blood or other fluids
Hemodynamic Management
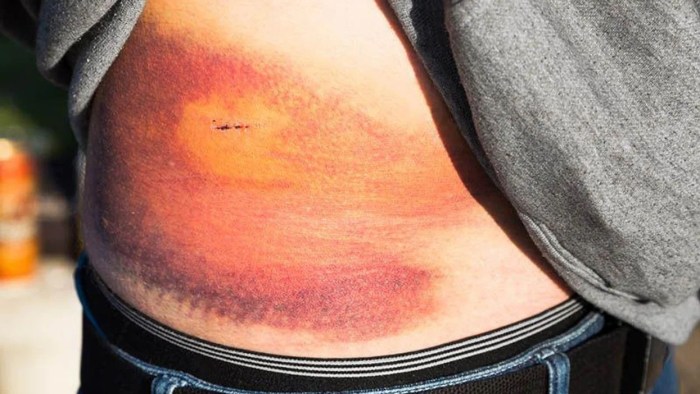
Hemodynamic management is crucial in patients with blunt abdominal trauma. The principles include:
- Fluid resuscitation:Aggressive fluid resuscitation with crystalloids or colloids to maintain intravascular volume
- Vasopressors:May be used to maintain blood pressure in cases of severe hypotension
- Blood transfusions:May be necessary to correct anemia and maintain oxygen delivery
Monitoring parameters used to assess hemodynamic status include:
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
- Central venous pressure (CVP)
- Urine output
- Base deficit
- Lactate levels
Common Queries
What are the common organ injuries associated with blunt abdominal trauma?
Common organ injuries include liver lacerations, splenic ruptures, kidney contusions, and bowel perforations.
What are the signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability in blunt abdominal trauma?
Signs and symptoms include hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, and decreased urine output.
What is the role of computed tomography (CT) in evaluating blunt abdominal trauma?
CT is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating blunt abdominal trauma, providing detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen and pelvis.